
Designed for ADHDers and non-ADHDers alike, this test will help you better understand ADHD, its symptoms, and its affects.
The quiz is all multiple choice questions, and you get your score at the end.
Thanks for playing!
Results

#1. True or False: ADHD is a Learning Disability
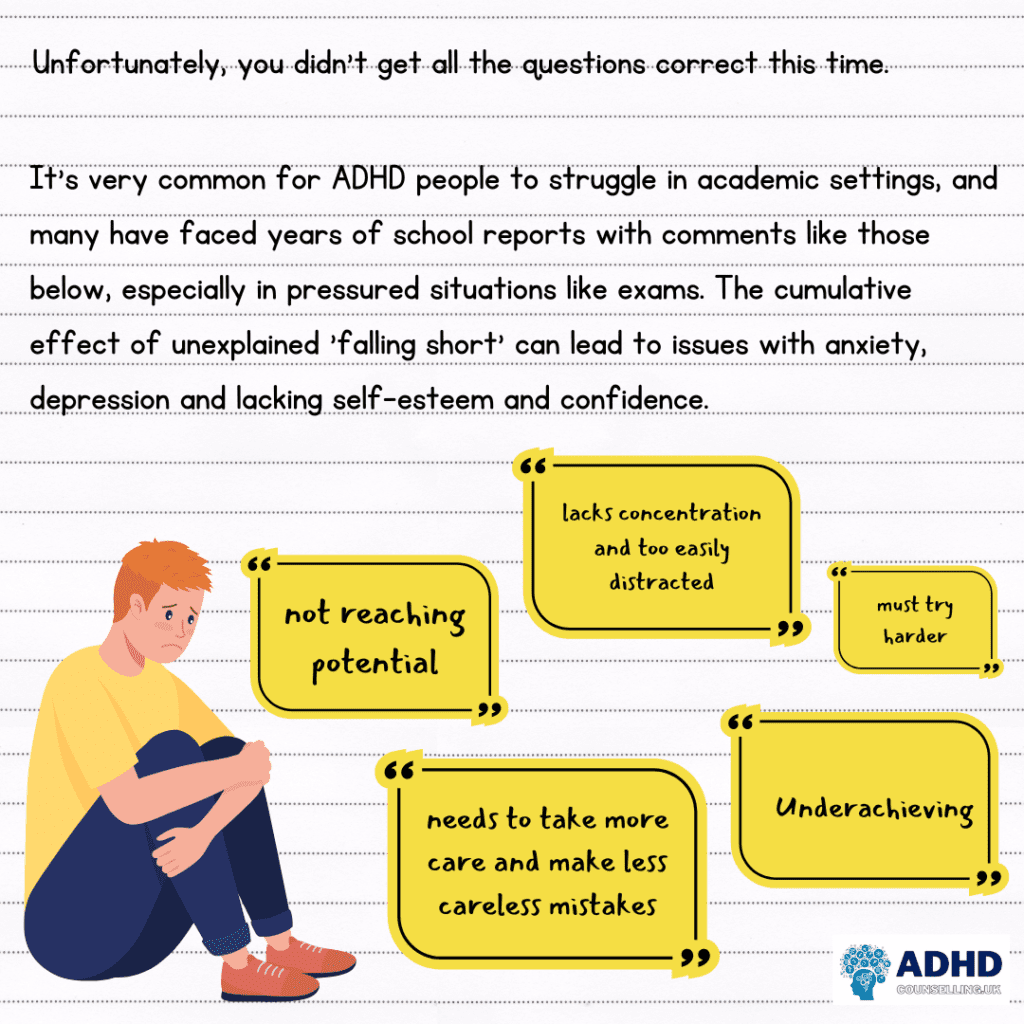
This is False.
ADHD does not affect a person’s ability to learn skills such as reading, writing or mathematics, although some of the effects of ADHD, such as difficulty focussing, can cause challenges in learning.
ADHD is categorised as a neurodevelopmental disorder, a term given to a group of disorders which affect development of the nervous system and lead to abnormal brain function, and may affect emotion, learning ability, self-regulation and memory.
#2. Research suggests ADHD is caused by…
Select all that apply:
Brain Structure and Function
Extensive research has shown clear structural differences in the ADHD brain, specifically focussing on brain size in people with ADHD, (more-so in ADHD children than ADHD adults) including the hippocampus and amygdala – the areas responsible for emotional processing and impulsivity.
Decreased blood flow has been observed to various areas of the brain in those with ADHD, indicating decreased brain activity. This differential in brain function is particularly observed in the prefrontal cortex, the area of the brain responsible for many tasks including cognitive control, attention and perseverance.
Environment
A common misconception is that nature and nurture have an equal role to play in the development of ADHD.
ADHD is not caused by issues in the home, or more common in troubled children.
That said, exposure to some chemicals or substances has been shown to have a link to the development of the condition, particularly with environmental toxins such as mercury, lead or pesticides.
Food Additives
Although evidence exists to connect consumption of food additives – more commonly referred to as ‘E Numbers’ – with hyperactivity and so some ADHD-like symptoms in children, there is no evidence to suggest that they actually cause ADHD.
Genetics
Evidence overwhelmingly suggests a genetic link in ADHD, with National Institute of Health (NIH) research showing that one third of fathers who have or had ADHD will have children with the condition.
Other research has shown that a child with ADHD is four times more likely than someone without ADHD to have a family member with the condition.
Immunisations
There is no evidence that vaccines cause ADHD. Evidence published in 1998 linking vaccines to Autism and ADHD were based on falsified data, for which the author lost his medical licence due to multiple conflicts of interest, and the paper was later withdrawn.
Premature Birth
Children born at 33 weeks or earlier have been shown in a wide-ranging study to be more likely to show symptoms of ADHD. It should be said, however, that this study did not later identify which, if any, of the participants were later diagnosed.
The link between premature birth and ADHD is more likely linked to the development of the brain.
Screen Time
Although exposure to screen time (such as televisions, mobile phones, or tablet computers) has been shown to negatively impact the development of attention in those 18 months and younger, the same research has similarly shown the positive effect of educational programming for cognitive, literacy and social outcomes in those 24 months and above.
There is no evidence to support a claim that you are more likely to develop ADHD as a result of spending too much time staring at a screen.
Sugar
No evidence exists to definitively link sugar with causing ADHD.
Consumption of sugar is however likely to cause an increase in the symptoms of ADHD in children. In later life, people with ADHD have been shown to have a significantly higher rate of excessive consumption of stimulant food and drink, including sugar.
Use of Alcohol or Nicotine During Pregnancy
With clear links between the healthy development of foetuses and alcohol use and/or smoking already long-established, research has subsequently shown ADHD development risk is 1.55 times higher in children of mothers who consume alcohol, and 2.64 higher if the mother smokes.
Video Games
This may surprise some, but the playing of video games, even to excess, does not cause ADHD.
That said, the nature of video games – an escape from reality, instant reward and visual stimulation, among others – are very appealing to the ADHD brain.
Additionally, video games can particularly help people with ADHD develop essential skills such as hand-eye coordination, strategy and problem solving, planning and prioritising, collaboration and time management.
#3. Likely symptoms of ADHD include…
Select all that apply:
All of the above are considered symptoms of ADHD, with the exception of lack of motivation.
In fact, behaviours associated with laziness or lack of motivation are likely to be anything but; motivation, creativity and intent are as present (if not more so) in ADHD people as those without the condition. However, the corrosive accumulation of repeated negative experience and the disconnect between intent and action may give the appearance of lacking drive or interest, but could be more accurately described as being ‘worn down’.
#4. True or false: we all have symptoms of ADHD
#5. Therefore, we could all be diagnosed with it
Although the individual components of ADHD are present and recognise able in most of us at one time or another, the criteria for an official diagnosis are vastly different to saying, for example, “we all get distracted sometimes”.
The difference is one of chronic behaviour; a rule rather than an exception.
To be officially diagnosed with ADHD, the person must display six or more of the listed nine characteristics of inattention, or six or more of the nine characteristics of hyperactivity and impulsivity.
In addition to this, conditions must be met that evidence:
- That these symptoms were present before the age of 12
- That symptoms were present in two or more settings – such a home, work, or with friends or in relationships
- That the symptoms clearly impair the quality of social, school or work functioning
- That the symptoms are not better explained by another mental disorder, such as anxiety or a personality disorder.
Following the successful meeting of these criteria, one of three diagnoses can be given:
- Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive Presentation
- Predominantly Inattentive Presentation
- Combine Presentation
#6. Is ADHD more common in men than in women?
The answer (technically) is yes.
However, with research historically focussed on men and boys, the statistics are skewed. What we also know is that women and girls are far more likely to be mis-diagnosed with another condition, and are less likely to display the disruptive external symptoms in childhood.
#7. True or false: Men and boys are three times as likely to be diagnosed with ADHD than women and girls?
This is true.
A 2015 research study in the UK of more than 10,000 children aged 5-15 found that 3.62% of boys had ADHD, while 0.85% of girls had the condition.
#8. The national average wait time for an ADHD assessment via the NHS is…
The current wait time for a diagnosis via the NHS is in excess of two years, and growing, with wait times in some parts of the UK as high as five years.
The ‘Right to Chose’ pathway (see here) can cut this wait time significantly.
#9. Which of the following conditions are associated with ADHD
Select all that apply:
More than two-thirds of people with ADHD have at least one other co-morbid condition.
Those diagnosed in adulthood will likely have lived a life full of challenges and difficulty, and feelings of anxiety, self-doubt, isolation and lacking self-esteem are extremely common, in addition to any number of other diagnosable conditions.
Rejection Sensitivity Dysphoria (RSD)
An extreme sensitivity to rejection or the even just the possibility of rejection, people with RSD in addition to their ADHD often over-compensate in their relationships in order to make people like and admire them.
Episodes of RSD are normally short and extremely powerful and those that have it report feeling easily embarrassed, have angry outbursts when they feel rejected, have low self-esteem, suffer with social anxiety, have issues in personal relationships, and are more prone to self-harming behaviours.
Misophonia
A condition in which the involuntary exposure to certain sounds trigger emotional or psychological responses which may be viewed as inappropriate to the situation in which they’re experienced. Sometimes referred to as Sound Sensitivity Syndrome, those with the condition may suffer from reactions such an angry outbursts, panic attacks, or a need to flee the source of the sound.
Oppositional Defiance Disorder (ODD)
More commonly diagnosed in childhood than present in adulthood (but nonetheless, a significant portion of adults continue to display symptoms of the disorder), ODD refers to a recurring pattern of involuntary negative, defiant and hostile behaviours towards figures of perceived authority. ODD differs from the similar Conduct Disorder (CD), a condition also associated with ADHD, but whose symptoms express more extremely – physical aggression towards people or animals, lying, stealing or destruction of property.
#10. True or False: ADHD can be cured
There is no cure for ADHD.
However, it is considered a highly treatable disorder.
Those who receive the right diagnosis and follow an appropriate treatment plan – for example a combination of therapy, medication and symptom management – can live comfortably, without their condition negatively impacting their lives.




